If you feel confused by the ever-changing data and recommendations surrounding COVID-19, you are not alone. As a new virus emerges, doctors and scientists are learning new information almost daily. Hence, the need to modify recommendations as this information arises.
If I say one thing to help guide you through this process, it is that as long as the virus is around, you must take measures to mitigate the risk of getting and spreading it. Over the last few months, many of us have witnessed two extremes: Those who drive alone in their car while wearing gloves, a mask, and a face shield, and those who partake in large group gatherings with no social distancing nor PPE of any kind.
Regardless of whether you fall into one of these categories or somewhere in the middle, I think we can agree that we all want to do whatever we can to keep our loved ones out of harm’s way.
The question I get asked the most from family and friends is regarding what measures to take when visiting with others. Whether it is a party for Grandma’s 90th birthday or a relatively small family gathering at a lake house, everyone wants to know a definitive answer on doing the right thing in the age of COVID-19.
Although there are evidence-based answers, anyone watching one of the numerous news networks or various social media feeds knows the research is ever-changing. Even those of us who have been critically reviewing journal articles as part of our career are relatively confused as to what the perfect answer is. As I said, you are not alone!
All of that being said, I would like to offer what I think is a risk-mitigating, comfort level approach to keeping you and your loved ones as safe as possible during group gatherings and family visits. For this, we need to make a few assumptions:
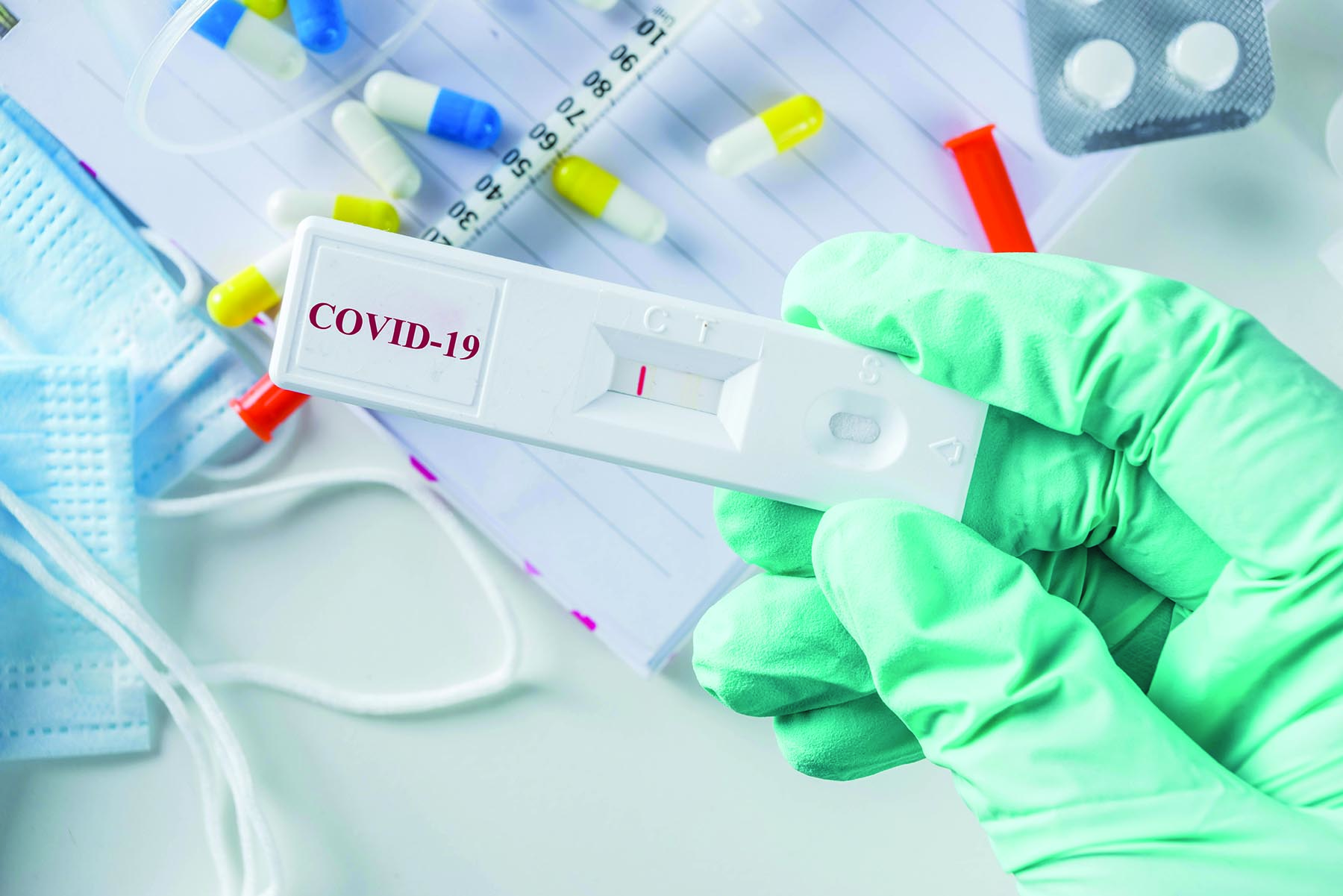
Assumption 1: When someone says they tested negative, assume this means they still could be infected with the virus.
Yes, I know this one is confusing, but it is very important. PCR and Rapid tests of all kinds (including flu) have always been known to be unreliable – this is not unique to COVID-19. This means that you should always inquire about symptoms, such as fever, cough, loss of smell/taste, etc. (refer to the CDC website for a current symptom list; cdc.gov/ coronavirus/2019-ncov/ symptoms-testing/ symptoms.html). If a person tests negative and has any of the listed COVID-19 symptoms, you must assume they are infected, and the test didn’t pick it up.
Assumption 2: Asymptomatic patients can still transmit the virus.
If someone says, “I tested positive but didn’t have any symptoms, therefore, I am fine,” be cautious. Although it seems that asymptomatic patients have a lower likelihood
of transmitting the virus, the evidence is debatable and from a personal standpoint, I wouldn’t bank on a lower potential transmission rate equating near zero chance, especially when dealing with any of the vulnerable populations. Play it safe!
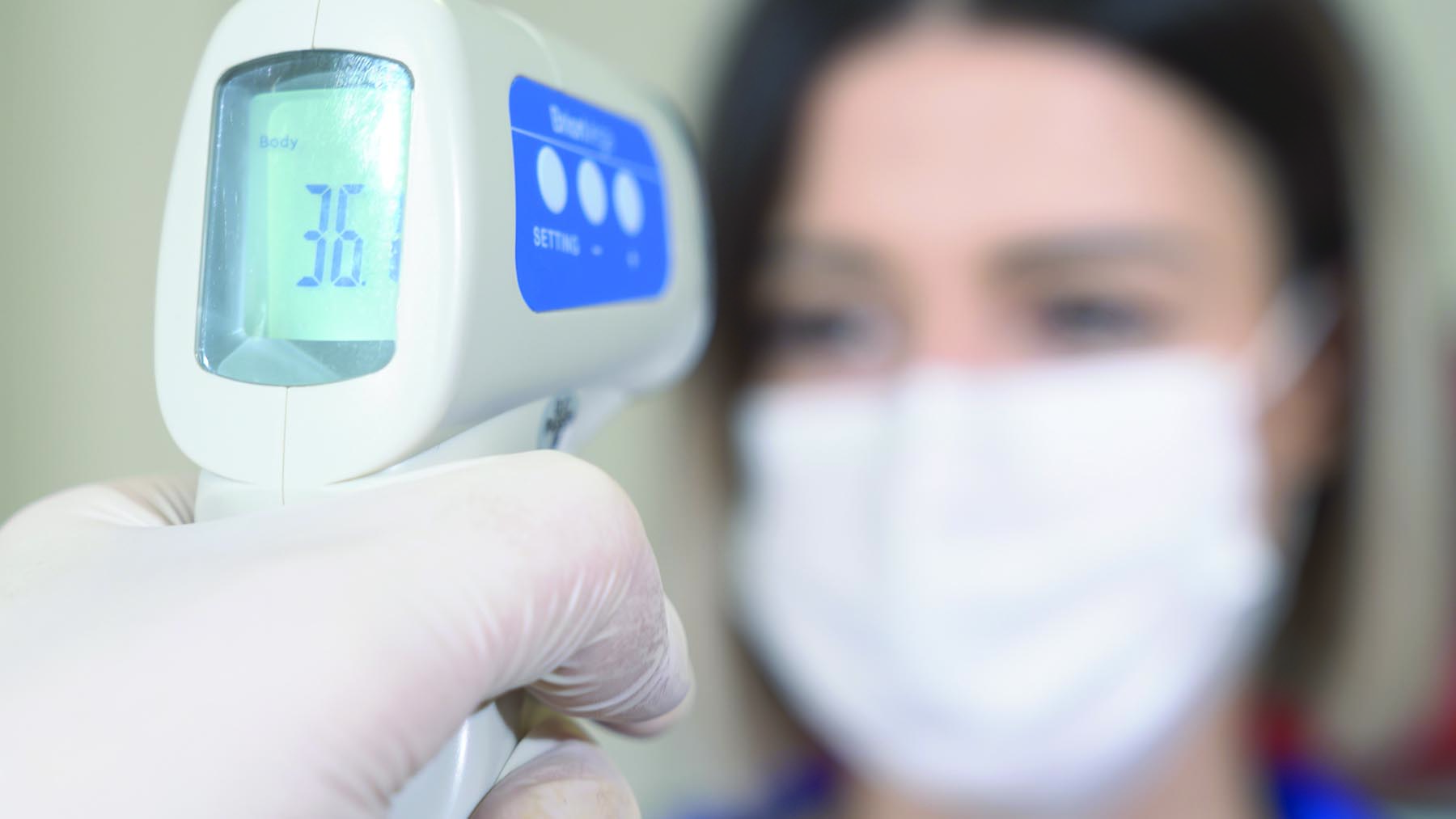
Assumption 3: Assume that anyone with a fever of 100.4°F or greater has COVID-19.
For those who are taking temperatures at their door, more power to you. Although it is surely an uncomfortable welcome at the front door, it is one of the few truly objective measures we can take, even if it won’t screen in every infected person. Understand though, a temperature of 99° Fahrenheit is not a true fever. I grew up thinking anything above a 98.6° meant you were hospital-bound. We all have very normal fluctuations in our core temperatures throughout the day, but a fever doesn’t truly start until 100.4° Fahrenheit.
Assumption 4: Assume everyone has COVID-19.
Clearly, this will be the most controversial assumption, but I believe a smart approach, especially when dealing with the elderly population and those with chronic illnesses, such as diabetes or lung disease. Assume everyone has COVID and take precautions based on that. Everyone may seem okay or say they are fine, but don’t stop practicing strict hand hygiene or whatever form of social distancing you usually partake in.
If you don’t personally believe this is as bad as the news is portraying, the simple effort of regular hand sanitizing/washing and wearing a face mask during group gatherings could have maximum outcomes if it means you could prevent the spread to a vulnerable person.
Should you worry so much about your healthy 3-year-old or 16-year-old getting very ill? Not nearly as much as the vulnerable populations, but you should worry about who they will potentially pass it on to. Thankfully, although children can indeed get ill, they seem to be the safest population when it comes to COVID-19 with mortality and morbidity rates seemingly lower than influenza, but this doesn’t mean that they are not vectors.
At the end of the day, we all want to keep our loved ones as safe as possible, but unless you live in a HEPA filter bubble, I don’t think there is a 100% perfect approach in this COVID world we live in; however, you can mitigate risk. Personal interactions are core to our sanity and mental health. If you understand the risks and take precautions to mitigate them when you can, you can certainly achieve these interactions while maintaining relative safety.
By Dr. Jahn Avarello
Dr. Avarello was the Division Chief of Pediatric Emergency Medicine for the Cohen Children’s Medical Center of NY for the past 9 years and is now the Florida Regional Medical Director for PM Pediatrics Urgent Care (1st site due to open in the Sawgrass Center this fall). He is currently seeing patients for acute care needs virtually at PMPanywhere.com.